Webserver tutorial
In this brief tutorial we will use the webserver to generate a hybrid structure and topology for a W6A mutation in a Trp-cage miniprotein. As a starting structure we will use an NMR ensemble 1l2y.pdb. Below is an image of the filled webserver query which would allow successfully generating hybrid structure and topology for this mutation. Next, this tutorial will go step-by-step over the available options: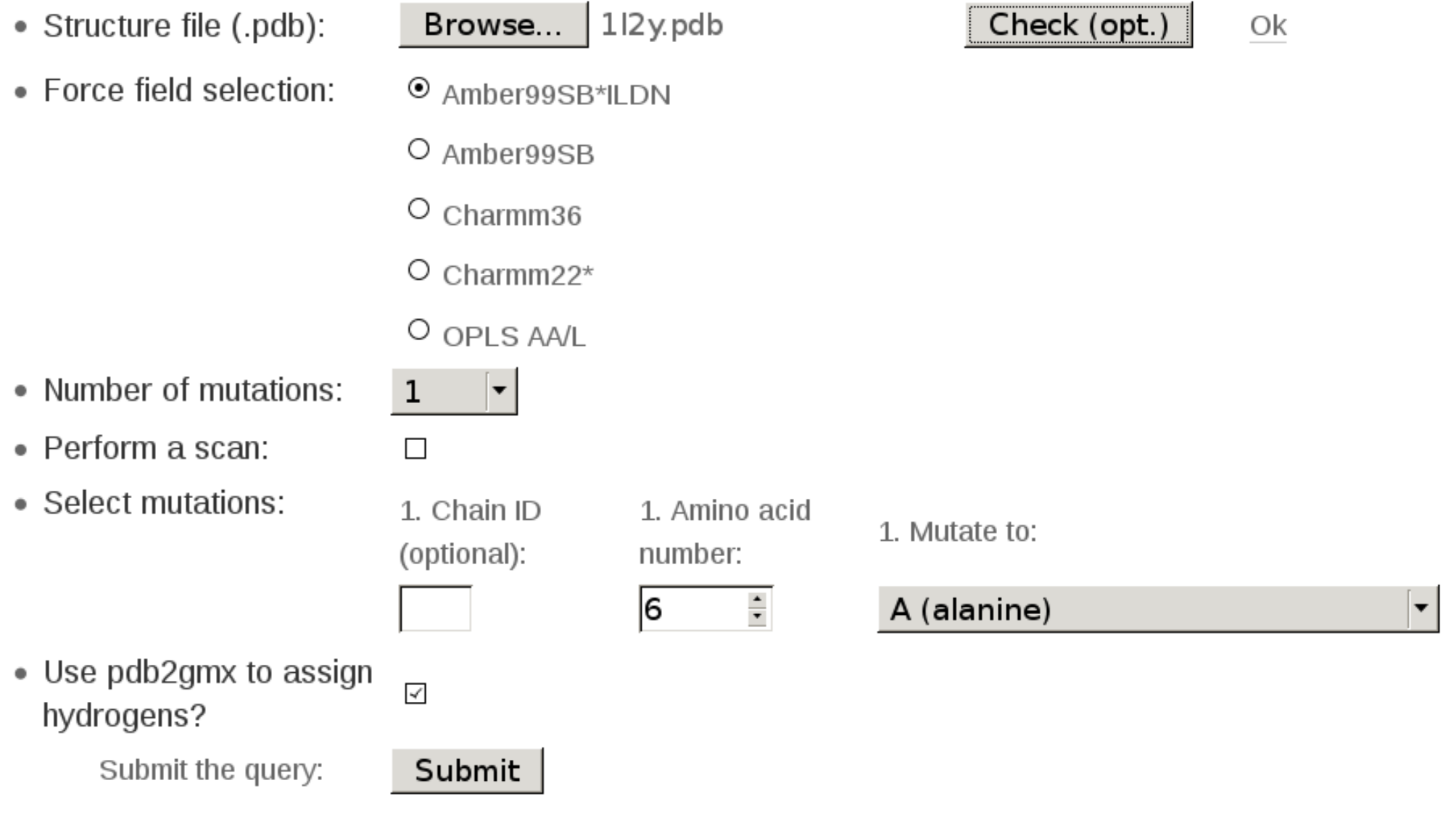
Firstly, find the structure 1l2y.pdb on your machine for submission to the webserver. The 1l2y NMR ensemble contains 38 conformers, however, the webserver will consider only the first one. It is also recommended to perform a structure checking step: Check (opt.) button. This option allows testing whether the selected structure would be properly processed by the webserver.

The structure checking step is optional, however, a quick execution of this test may provide some useful information. For example, in case of the 1l2y.pdb structure, the webserver informs that the structure check was successful. By clicking 'Ok' you may find some additional information:

For this case the webserver informs that it would be able to process the structure, but the "Use pdb2gmx to assign hydrogens?" box must be checked.
In the following step you need to choose one of the molecular mechanics force fields. More information about the force fields is provided in the Instructions section.

Next, we define one mutation to be made. The webserver allows performing an arbitrary number of mutations at once. Up to three mutations can be entered interactively. More mutations could be entered in a web-based form. Note, however, that introducing several mutations at once will slow down convergence of the free energy estimates. It often is a better idea to perform the mutations in a one-by-one manner.

We keep the "Perform a scan" option de-selected, as in this example we are interested in a single mutations.

To define an amino acid to be mutated you may provide a chain ID together with a residue number. Chain ID is optional: if not given, the webserver will search for the first residue in the structure that has a number matching the provided one. In this case we can simply provide an amino acid #6, because 1l2y structure contains only one chain. The dropdown menu allows to select the desired mutation. The unsupported mutations are excluded from this dropdown menu, e.g. prolines, glycines for the Charmm family force fields (see Instructions).

If a structure has no hydrogens the "Use pdb2gmx to assign hydrogens?" box needs to be checked. Also, this option may be required if hydrogen atom naming in the submitted strucure is not recognized by pdb2gmx. In the case of the 1l2y.pdb structure, the structure checking step has already informed us that this box must be set for a successful structure processing.

Once the query is submitted, you should see a new window with the following information:

The created hybrid structure/topology can be downloaded by following the generated link. Note, that your files will be stored on the webserver only for 7 days.